There are several options for transformers on the market, including toroids, bobbins, and solenoids. Why choose one over the other? Out of the above three, toroids are most frequently used because of their many benefits and a small number of cons. Understanding the basics of a toroidal transformer can help you get better transformers for your products and applications.
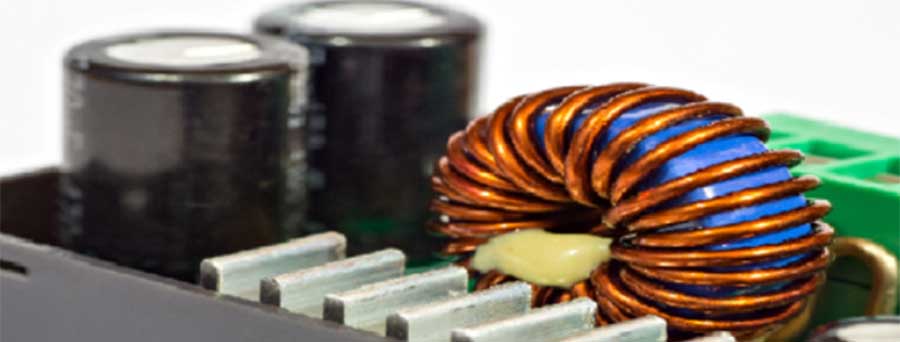
Simply put, a toroidal transformer can be used in any electronic transformer application that can house the size and shape of a toroid. Although a toroid can work in these settings, it is not always ideal. Our team can help you decide if toroids are right for you.
There are standard materials used when creating toroidal transformer cores, including silicon steel, iron powdered, ferrites, and amorphous, but the construction of toroids is not limited to conventional materials. We use all the materials available to us, which includes moly-permalloy powder, nickel-iron, and more. Ask us about your material concerns.
A toroid is a circle with a hole poked out of it (like a doughnut), and it has 360 degrees of wound wire. The closed circle allowed for a near complete magnetic field that is canceled outside the coils. The circular shape lessens EMI when compared to other transformer types.
There is a time a place for toroids. We can help you with all your transformer winding needs.
Related Reading Toroids
- Uncommon Toroid Benefits
Those that have used toroids before can quickly rattle off many of the advantages these transformers have over their counter parts. There are more than just a few good reasons to consider using custom coil winding and toroidal transformers when constructing and designing electronic devices. - Why do Toroidal Transformers Stand Out from Other Transformers
- Why a Donut Shape is Ideal

